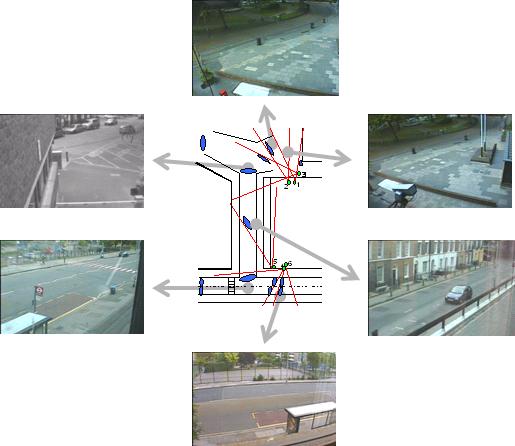
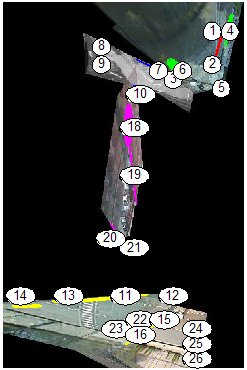
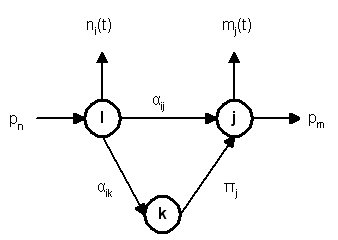
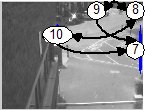
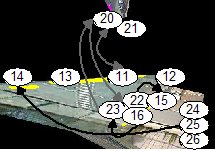
The knowledge of the detected links
reveals the camera topolofy of the system:
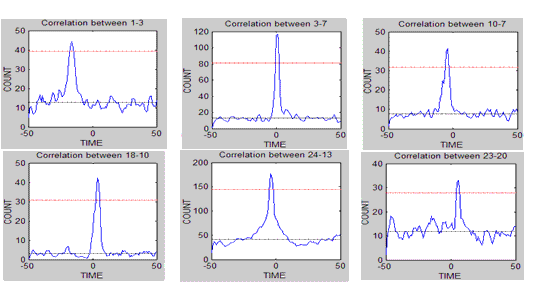
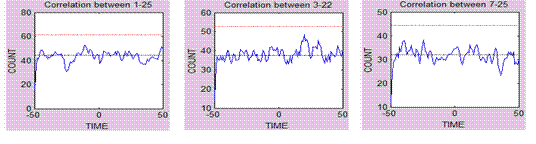
The following figures show the detected links between nodes for a
single camera and for three differrent cameras. It is interesting that
no tracking information has been used to estimated the links, only
cross-correlation of events in different areas.
Tracking example
Publications
About