Aim
To learn activity-based semantic scene features of a scene from large
sets of observations automatically.Introduction
In old-style surveillance, human personnel is responsible to monitor the activity of the scene through a set of cameras and look out for unusual events. Also, quite often they have to go through recorded video data and gather information and evidence for specific events. However both tasks are quite tedious and boring, therefore it is inevitable that interesting events are overlooked.Potentially, these problems could be tackled by automated visual surveillance systems with high level capabilities such as to detect suspicious events and alarm the personnel, annotate and encode events in a way that facilitates the interaction with the human operators.
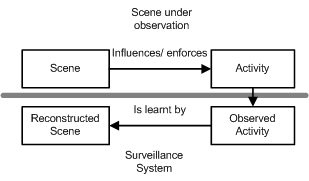
Here, we discuss how a semantic scene model can be learnt automatically from observations and how such a model can be used for a variety of applications.
Semantic Dictionary for Visual Surveillance
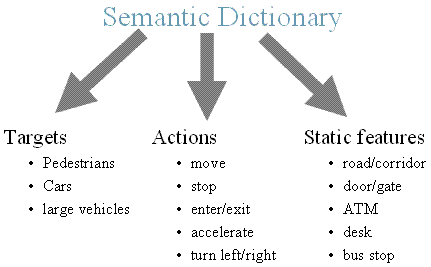
The semantics that are of interest in a surveillance
system can be classified into three categories: Targets (e.g
pedestrians, cars, large vehicles), Actions (e.g. move, stop,
enter/exit, accelerate, turn left/right)
and Scene Static features (e.g. road, corridor, door, gate, ATM, desk, bus stop). The proposed general scheme is that Targets perform Actions in a environment consisting of other targets and scene static features. This work is mainly about learning the scene static features.
Firstly, to exploit the vast amount of observations that are available due to the continuous operation of the surveillance system.
Secondly, to allow the development of systems that can automatically learn their environment so they can be easily installed (plug’n’play) and adapt.
and Scene Static features (e.g. road, corridor, door, gate, ATM, desk, bus stop). The proposed general scheme is that Targets perform Actions in a environment consisting of other targets and scene static features. This work is mainly about learning the scene static features.
Learning in Visual Surveillance
We suggest that learning in Visual Surveillance must be performed mainly unsupervisedly, for two reasons:Firstly, to exploit the vast amount of observations that are available due to the continuous operation of the surveillance system.
Secondly, to allow the development of systems that can automatically learn their environment so they can be easily installed (plug’n’play) and adapt.